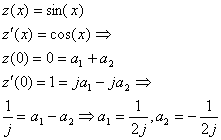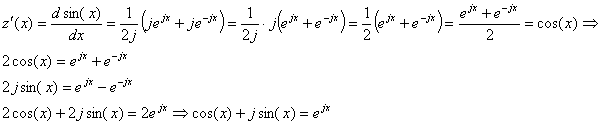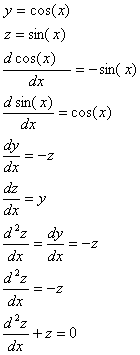
The last equation is a homogeneous linear second order differential equation with constant coefficients:
![]()
where
![]()
For these simple equations, we look for a solution of the form
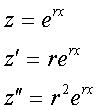
Substituting these values we get
![]()
Dividing through by ![]() gives
gives
![]()
which is the characteristic equation of the differential equation.† The solution of this equation can be derived from the quadratic equation
![]()
Substituting the values gives
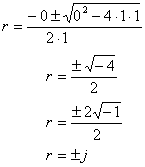
The two solutions to the differential equation are
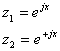
And the complete solution is
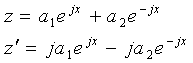
Recalling that